-

Sustainable IT Sourcing Alignment with Responsible Computing
Written by: Clint Pegram
Technology has become integrated and integral to our daily lives. Key drivers such as COVID19, data privacy, climate change has created opportunities for companies to revisit their business models to create digital experience with the customer. The consumer expectation has also increased usage of technology has prompted companies to use technology responsibly.
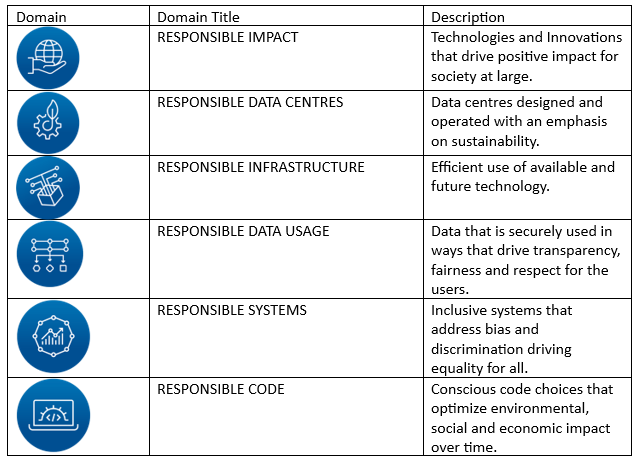
To guide companies towards using technology in a responsible manner, a consortium was established which led to the development of the Responsible Computing Self-Assessment. The assessment includes 6 domains which details goals, approach and benefits of each domain, with a number of questions. The self-assessment allows the company to develop a baseline of their sustainability readiness within their existing computing environment.
Here is a brief overview of the 6 pillars [i]are
When we consider global economy, a key component of global trade is the sourcing of raw materials . As companies develop their products and services, a value chain is created which refers to the various business capabilities required in creating a product or service for the market. These business capabilities would include the processes, organisation team, technology and key performance indicators to measure the success of the product or service. The value chain as per Michael Porter[ii] creates value for the business and customer, and includes the following primary and secondary stages:
The primary stage focuses on the creation, delivery, and service of the product or service. The activities of the primary stage include Inbound Logistics (receiving of rate material) , Operations (transforming raw material into finished product), Outbound Logistics ( packing, shipping to market) , Marketing and Sales (promotions, advertising, sales) and Services (personnel training, customer service).
The secondary stage focuses on the procurement, people, and infrastructure activities. The activities of the secondary stage include Procurement (sourcing of raw material), Technology Development (research and development), Human Resource Management (recruitment, hiring) and Infrastructure (financing and planning).
The above highlights the key stages of sourcing from primary to secondary activities. One can only imagine how complex the sourcing can be between the company and related partners. As we navigate the various stages of sourcing, we are able to identify the greenhouse gases emitted. The gases are identified as:
Scope 1 – Direct emissions from assets owned by the company which can include buildings, equipment and vehicles.
Scope 2 – Refers to indirect emissions from purchasing services such as electricity.
Scope 3 – Refers to emission that occur in the organisations value chain. These activities relate to emissions that are produced from the various partners the organisation deals with from a sourcing point of view.A report from the World Economic Forum (WEF)[iii] indicates that “Scope 3 emissions typically account for more than 70% of a business’s carbon footprint”.
The WEF identified 4 actionable areas to focus to reduce Scope 3 emissions. They:
- Start from Within
- Automate existing data reporting
- Drive a green product design revolution
- Engage in sustainable business model innovation
- Empower your supply chain
- Foster a partnership mindset.
- Become a role model in supply chain transparency.
- Leverage industrial ecosystems
- Engage in Scope 3 standards harmonisation
- Build product carbon footprint data exchange capability
- Support sustainable innovation and infrastructure
- Drive the cultural shift towards a sustainable society
- Shift mindsets to unlock business value beyond costs
- Rethink consumptions and make green choices easy for consumers
A research opportunity exists, and will be the focus of an upcoming Responsible Computing whitepaper on ‘Responsible IT Sourcing’. By continually applying a sustainability lens to every aspect of our IT infrastructure, we can nudge our collective organizations towards more responsible behavior.
ENDNOTE
[i] “Our Domain Provides Guidance on Key Performance Indicators and Pathways”, https://responsiblecomputing.net/domain/ , (Accessed 14 December 2023)
[ii] “What is a Value Chain Analysis”, https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-value-chain-analysis, (Accessed 14 December 2023)
[iii] World Economic Forum (WEF), “The “No-Excuse” Opportunities to tackle Scope 3 Emissions in Manufacturing and Value Chains“, December 2023
- Start from Within
-

Sustainable IT Sourcing Alignment with Responsible Computing
